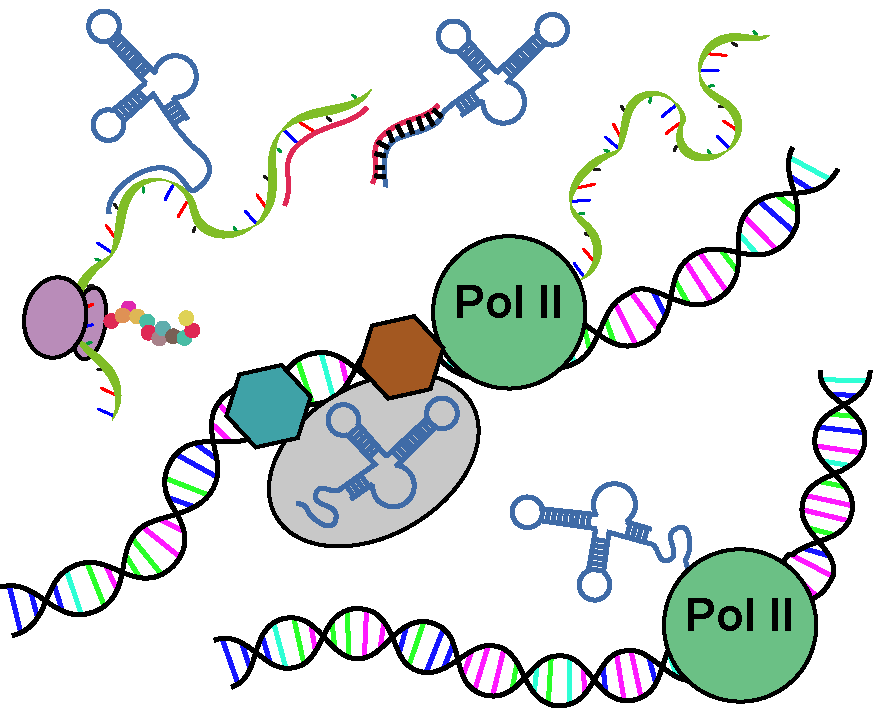
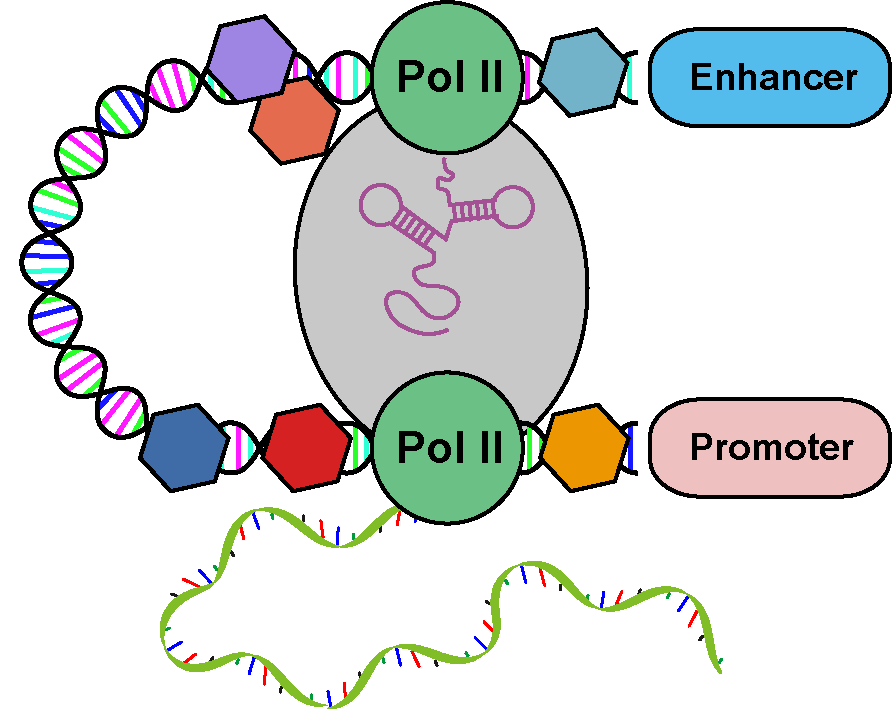
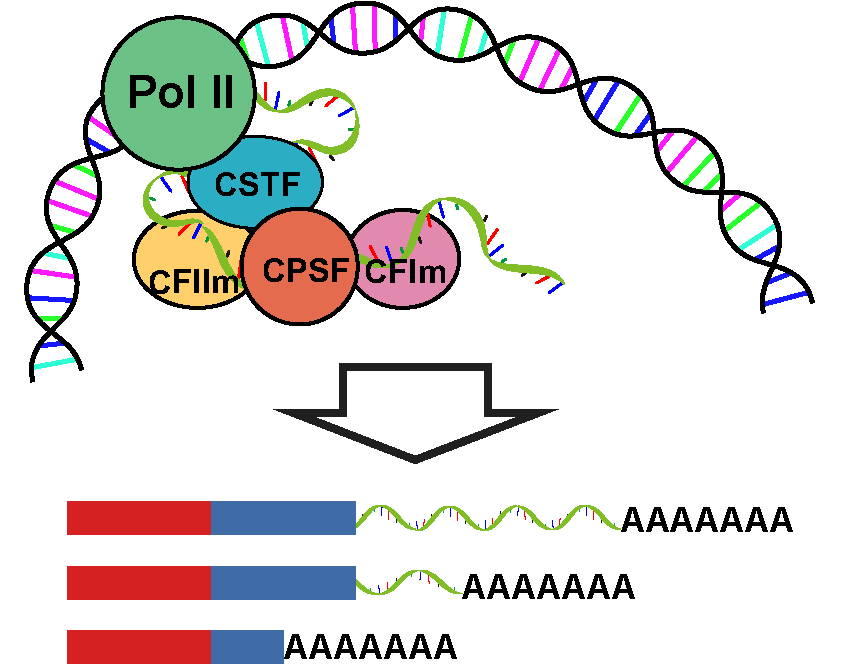
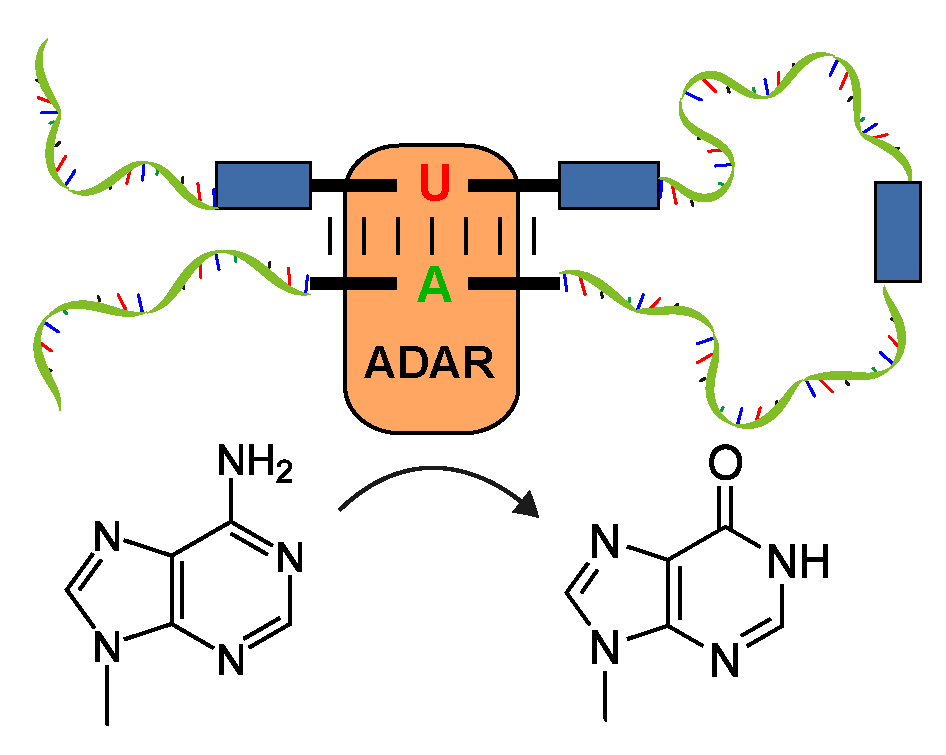
ADAtlas
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder and the most common dementia among the elderly. Accumulating researches indicate that broad transcriptional dysregulation happens in AD process, highlighted AD-related molecular pathways and gene expression networks. Here we characterized the landscape of lncRNA, enhancer RNA (eRNA), alternative polyadenylation (APA), and A-to-I RNA editing in AD brain samples, and highlighted differential non-coding RNAs and post-transcription regulation events among AD stages. We also analyzed the correlation between non-coding RNAs/post-transcriptional regulation events and protein coding gene expression. These non-coding RNAs and post-transcriptional regulation events may uncover novel mechanisms for the transcription dysregulation and regional vulnerability in AD process.